Key Autism and EMF Papers
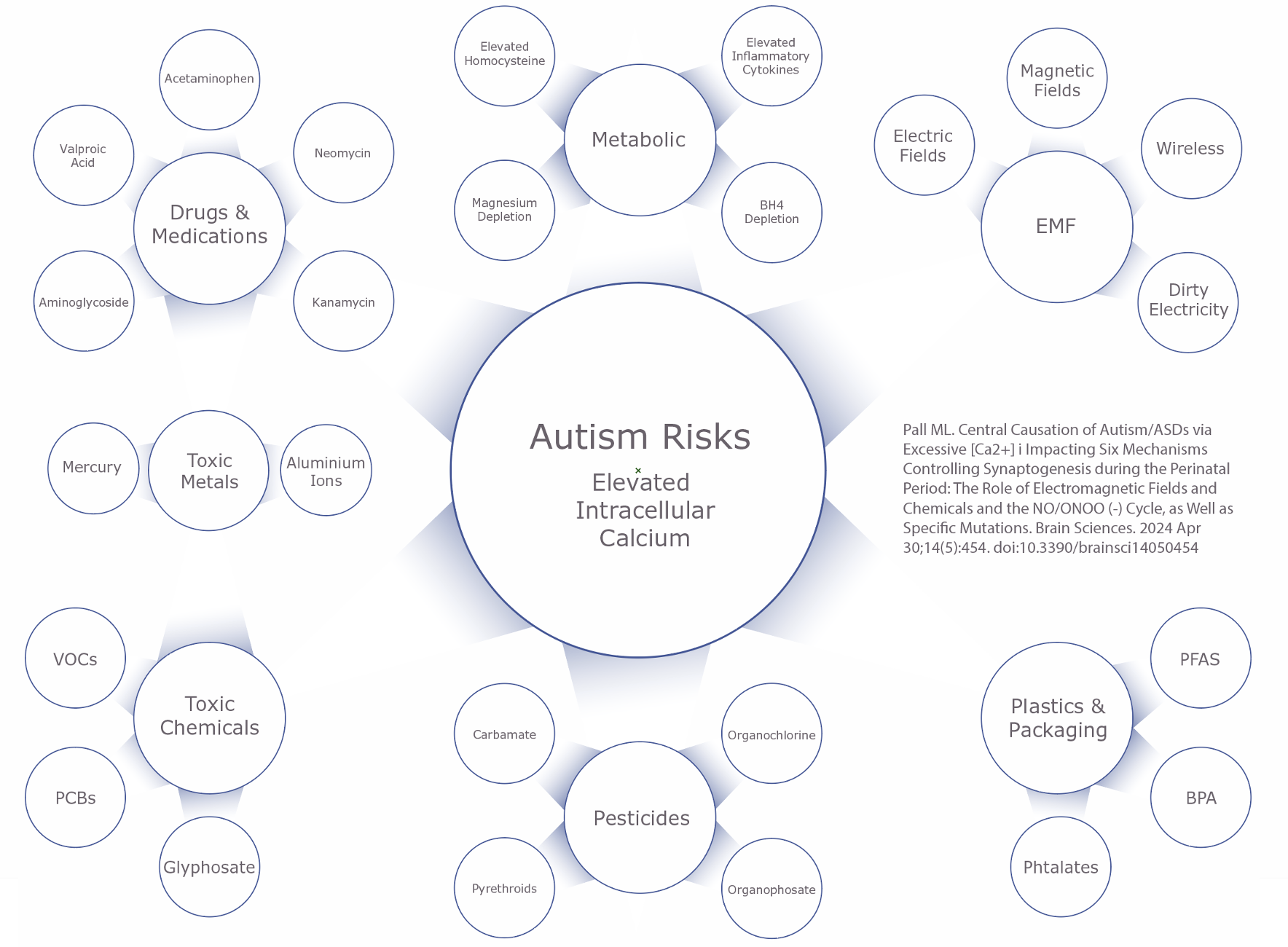
Pall ML. Central Causation of Autism/ASDs via Excessive [Ca2+] i Impacting Six Mechanisms Controlling Synaptogenesis during the Perinatal Period: The Role of Electromagnetic Fields and Chemicals and the NO/ONOO (-) Cycle, as Well as Specific Mutations. Brain Sciences. 2024 Apr 30;14(5):454. doi:10.3390/brainsci14050454
Summary: Excess intracellular calcium ions disrupt synapse development. EMF acts via voltage gated calcium channels to dysregulate and elevate intracellular calcium levels. Additionally, 15 chemicals (which include: mercury, aluminum, glyphosate and acetaminophen) are known to also elevate intracellular calcium via NDMA receptors.
Note: This paper focuses on excess intracellular calcium as the central cellular level mechanism in autism and explains how the total load of many of the primary environmental suspects (and some new suspects) work together to impact synapse development. The concept of intracellular calcium leading to excitement and excitotoxicity is in alignment with autism research findings of an imbalance of excitation and inhibition.
Herbert MR, Sage C. Autism and EMF? Plausibility of a pathophysiological link–Part I. Pathophysiology. 2013 Jun 1;20(3):191-209. doi:10.1016/j.pathophys.2013.08.001
Herbert MR, Sage C. Autism and EMF? Plausibility of a pathophysiological link Part II. Pathophysiology. 2013 Jun 1;20(3):211-34. doi:10.1016/j.pathophys.2013.08.002
Summary: The paper argues for a plausible link between Autism Spectrum Conditions (ASCs) and exposure to electromagnetic and radiofrequency radiation (EMF/RFR) by documenting the striking parallels between the multileveled biological disturbances found in both, including oxidative stress, mitochondrial and immune system dysfunction, inflammation, and calcium channel dysregulation.
Note: Breaching of the blood brain barrier may give some toxins and infectious agents access to brain tissue. This may mean that environmental factors that are not rising in the environment or are even declining in the environment, may have more access to brain tissue then they had in the past.
The following link is the original full paper, before it was shortened and broken into 2 parts for publication:
Key EMF Papers
Panagopoulos DJ, Johansson O, Carlo GL. Polarization: a key difference between man-made and natural electromagnetic fields, in regard to biological activity. Scientific Reports. 2015 Oct 12;5:14914. doi: 10.1038/srep14914
Summary: The polarization and coherence of man-made (anthropogenic) electromagnetic fields is a key factor that explains the disruption of voltage gated ion channels, which lead to a cascade of adverse biological effects at much lower power levels than natural EMFs, like sunlight.
Panagopoulos DJ, Yakymenko I, De Iuliis GN, Chrousos GP. A comprehensive mechanism of biological and health effects of anthropogenic extremely low frequency and wireless communication electromagnetic fields. Frontiers in Public Health. 2025 Jun 4;13:1585441. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2025.1585441
Summary: Man-made EMFs harm cells when polarization, coherence, and resonance align, activating VGICs via forced oscillation and driving oxidative stress, DNA damage, and disease.
Autism / Neurodevelopment and EMF Papers
Cakir B, Tanaka Y, Choe MS, Kiral FR, Kim J, Micali N, Kang YJ, Dharmadhikari B, Patterson B, Yang WS, Cho Y. Radiofrequency regulates the BET-mediated pathways in radial glia differentiation in human cortical development. Cell Reports. 2025 Oct 28;44(10). doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116238
Laván D, Argüelles N, Lluncor A, Huaman D, Moyano J, Ubillus J, Peña M, Paredes M, Hernández I, Guerra A, De La Cruz-Vargas J. Review of the evidence on the influence of Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz radiation on oxidative stress and its possible relationship with Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Neurology. 2025 Oct 3;16:1616435. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1616435
Setia R, Kaur H, Tandon S, Narang S. Radiofrequency electromagnetic field emissions and neurodevelopmental outcomes in infants: a prospective cohort study. Cureus. 2025.
Gallastegi M, Ibarluzea J, Santa Marina L, Villanueva CM, Guxens M. Characterisation of exposure to non-ionising electromagnetic fields in the Spanish INMA birth cohort: study protocol. arXiv preprint. 2025.
Pall ML. Central causation of autism via excessive intracellular calcium and electromagnetic fields & chemicals. Brain Sciences. 2024;14(5):454. doi:10.3390/brainsci14050454
Pietramala S, Zaffina S, Caretto A, Parisi P. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field treatment in children with autism spectrum disorder: a pilot study. Brain Sciences . 2024.
Özgün A, Marote A, Behie LA, Salgado A, Garipcan B. Extremely low frequency magnetic field induces human neuronal differentiation through NMDA receptor activation. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019 Oct;126(10):1281-1290. doi: 10.1007/s00702-019-02045-5.
Birks L, Divan HA, Kheifets L, Olsen J, Rapoport BI, Sahin N, et al. Maternal cell phone use during pregnancy and child behavioral problems in five cohorts. Environment International. 2017;104:122–131.
Mortazavi GH, Haghani M, Rastegarian N, Zarei S, Mortazavi SM. Increased release of mercury from dental amalgam fillings due to maternal exposure to electromagnetic fields as a possible mechanism for the high rates of autism in the offspring: introducing a hypothesis. Journal of Biomedical Physics & Engineering. 2016 Mar 1;6(1):41.
Huss A, van Eijsden M, Guxens M, Beelen R, Kromhout H, Vermeulen R. Environmental radiofrequency electromagnetic fields exposure and sleep in 7-year-old children: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0139869. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0139869
Alsaeed I, Al-Ahmari A, Alshahrani M, Alzahrani A, Alzahrani H, Alzahrani J, et al. Autism-relevant social abnormalities in mice exposed to extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience. . 2014;37:58-64..
Herbert MR, Sage C. Autism and EMF? Plausibility of a pathophysiological link – Part I. Pathophysiology. 2013;20(3):191–209. doi:10.1016/j.pathophys.2013.08.001
Herbert MR, Sage C. Autism and EMF? Plausibility of a pathophysiological link – Part II. Pathophysiology. 2013;20(3):211–234. doi:10.1016/j.pathophys.2013.08.002
Ahuja YR, Sharma S, Bahadur B. Autism: An epigenomic side-effect of excessive exposure to electromagnetic fields. International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. 2013 Apr;5(4):171-7.
Aldad TS, Gan G, Gao XB, Taylor HS. Fetal radiofrequency radiation exposure from 800-1900 mhz-rated cellular telephones affects neurodevelopment and behavior in mice. Scientific Reports. 2012 Mar 15;2(1):312. doi:10.1038/srep00312
Sparks RA. RF Energy Exposure and Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders. 2012.
Lathe R. Microwave Electromagnetic Radiation and Autism. E-Journal of Applied Psychology. 2009 Mar 1;5(1).
Divan HA, Kheifets L, Obel C, Olsen J. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to cell phone use and behavioral problems in children. Epidemiology. 2008;19(4):523–529. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e31817f6c8b
Carlo GL, Mariea TJ. Wireless radiation in the aetiology and treatment of autism: Clinical observations and mechanisms. Journal of the Australasian College of Nutritional and Environmental Medicine. 2007 Aug;26(2):3-7.
Thornton IM. Out of time: a possible link between mirror neurons, autism and electromagnetic radiation. Medical Hypotheses. 2006 Jan 1;67(2):378-82.
Kane RC.A possible association between fetal/neonatal exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation and the increased incidence of autism spectrum disorders. Medical Hypotheses. 2004;62(2):195–197.